Content delivery networks (CDN) are the transparent backbone of the Internet in charge of content delivery. Whether we know it or not, every one of us interacts with CDNs on a daily basis like when reading articles on news sites, shopping online, watching YouTube videos or perusing social media feeds. No matter what we do, or what type of content we consume, chances are that we will find CDNs behind every character of the text, every image pixel and every movie frame that gets delivered to our PC and mobile browser.
CDN is designed to solve the latency which is the annoying delay that occurs from the moment you request to load a web page to the moment its content actually appears on the screen. That delay interval is affected by a number of factors, many being specific to a given web page. In all cases, however, the delay duration is impacted by the physical distance between you and that website’s hosting server. A CDN’s mission is to virtually shorten that physical distance, the goal being to improve site rendering speed and performance.
To minimize the distance between the visitors and your website server, a CDN stores a cached version of its content in multiple geographical locations known as PoPs. Each PoP contains a number of caching servers responsible for content delivery to visitors within its proximity. In, essence, CDN puts your content in many places at once, providing superior coverage to your users. For example if someone in the Middle East is accessing your UK-hosted website, it is done through a local UK PoP. This is much quicker than having the visitor’s request, and your responses, travel the full width of the Atlantic and back.
Today, over half of all traffic is already being served by CDNs. Those numbers are rapidly trending upwards with every passing year. Content delivery networks are used for B2B interactions and in serving content to consumers. Today, as more aspects of daily life move online, organizations use the content delivery network to accelerate static content, dynamic content, mobile content, e-commerce transactions, video, voice, games and so on. Most websites tend to operate on a larger scale, making CDN usage a popular choice in the following sectors:
CDNs can assure better delivery of the contents (Video, OTT, streaming or websites) by delivering closer to the customers while also providing a big number of features to be used for marketing, add or optimization.
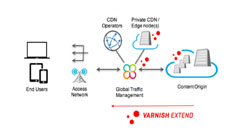
Private CDN